-
Table of Contents
Unlocking the Power Within: Exploring the Gut-Brain Connection
Introduction:
Gut Health Awareness: Understanding the Gut-Brain Connection
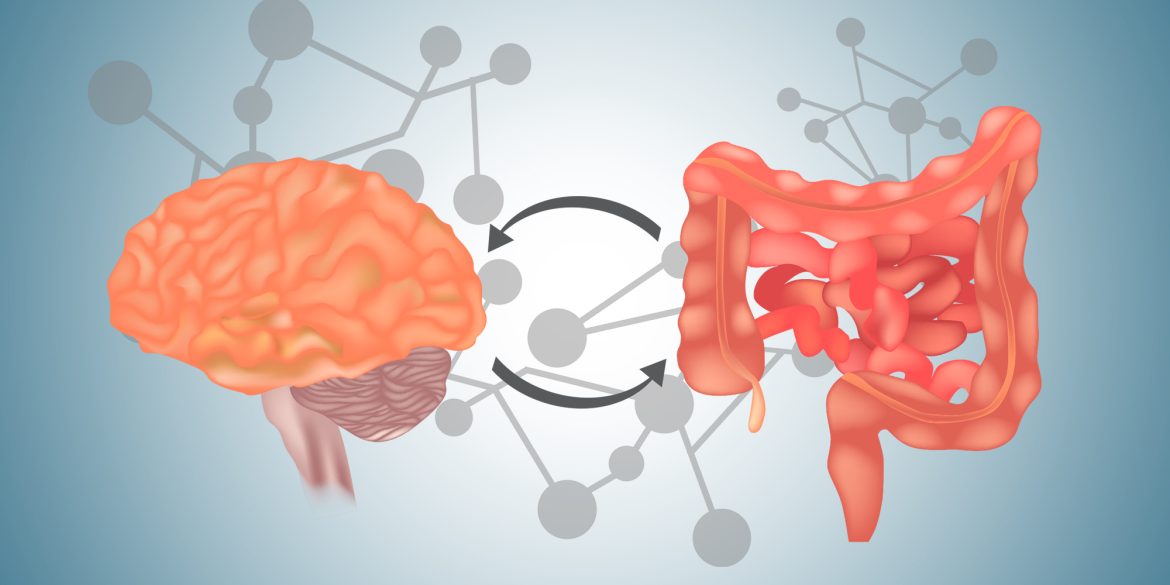
Gut health has gained significant attention in recent years due to its crucial role in overall well-being. The gut-brain connection, a complex and intricate relationship between the gut and the brain, has emerged as a fascinating area of research. This connection highlights the bidirectional communication between these two vital organs, emphasizing the impact of gut health on mental and emotional well-being. Understanding the gut-brain connection is essential for promoting gut health awareness and exploring potential interventions to improve both physical and mental health. In this article, we will delve into the significance of the gut-brain connection and its implications for overall health and well-being.
The Impact of Gut Health on Mental Well-being
The Impact of Gut Health on Mental Well-being
In recent years, there has been a growing awareness of the gut-brain connection and its impact on mental well-being. It is now widely recognized that the health of our gut plays a crucial role in our overall mental health. This connection is not surprising when we consider that the gut is often referred to as our “second brain.”
The gut-brain connection is a bidirectional communication system between the gut and the brain. It involves a complex network of nerves, hormones, and chemicals that constantly send signals back and forth. This communication is essential for maintaining a healthy balance in both our physical and mental states.
One of the key factors in this connection is the gut microbiota, which refers to the trillions of bacteria and other microorganisms that reside in our digestive system. These microorganisms play a vital role in maintaining the health of our gut and have a direct impact on our mental well-being.
Research has shown that an imbalance in the gut microbiota, known as dysbiosis, can lead to various mental health issues such as anxiety, depression, and even neurodevelopmental disorders like autism. This is because the gut microbiota produces neurotransmitters, such as serotonin and dopamine, which are crucial for regulating mood and emotions.
Furthermore, the gut microbiota also influences the production of other chemicals in the body, such as short-chain fatty acids. These fatty acids have been found to have anti-inflammatory properties and can help reduce inflammation in the brain, which is often associated with mental health disorders.
In addition to the gut microbiota, the gut-brain connection is also influenced by the gut barrier function. The gut barrier acts as a protective barrier, preventing harmful substances from entering the bloodstream. When the gut barrier becomes compromised, it can lead to a condition known as leaky gut syndrome.
Leaky gut syndrome allows toxins, bacteria, and undigested food particles to leak into the bloodstream, triggering an immune response and inflammation. This inflammation can then affect the brain, leading to symptoms such as brain fog, memory problems, and mood disorders.
Moreover, chronic stress, which is known to have a detrimental effect on mental health, can also impact gut health. Stress activates the body’s fight-or-flight response, which can disrupt the balance of the gut microbiota and compromise the gut barrier function. This, in turn, can further exacerbate mental health issues.
Fortunately, there are steps we can take to improve our gut health and, consequently, our mental well-being. One of the most effective ways is through a healthy diet. Consuming a diet rich in fiber, fruits, vegetables, and fermented foods can promote the growth of beneficial bacteria in the gut and support a healthy gut microbiota.
Additionally, managing stress through techniques such as meditation, exercise, and adequate sleep can also have a positive impact on gut health. These practices help reduce inflammation and promote a healthy balance in the gut-brain communication system.
In conclusion, the gut-brain connection is a fascinating and vital aspect of our overall well-being. Understanding the impact of gut health on mental well-being is crucial for promoting optimal mental health and preventing mental health disorders. By taking care of our gut through a healthy diet, stress management, and other lifestyle choices, we can support a healthy gut-brain connection and improve our mental well-being.
Exploring the Link Between Gut Health and Emotional Health
Gut Health Awareness: Understanding the Gut-Brain Connection
Exploring the Link Between Gut Health and Emotional Health
In recent years, there has been a growing awareness of the importance of gut health and its impact on overall well-being. While most people associate gut health with digestion and physical health, emerging research suggests that there is a strong connection between gut health and emotional health. This link, known as the gut-brain connection, has significant implications for our understanding of mental health and the potential for new treatment approaches.
The gut-brain connection refers to the bidirectional communication between the gut and the brain. This communication occurs through a complex network of nerves, hormones, and chemicals. The gut, often referred to as the “second brain,” contains millions of neurons that can influence our emotions, mood, and even behavior. Conversely, the brain can also influence the gut, affecting digestion and gut function.
One of the key players in the gut-brain connection is the gut microbiota, the trillions of microorganisms that reside in our digestive system. These microorganisms play a crucial role in maintaining gut health and have been found to have a profound impact on our mental well-being. Research has shown that imbalances in the gut microbiota, known as dysbiosis, are associated with various mental health conditions, including anxiety, depression, and even autism spectrum disorders.
How exactly does the gut microbiota influence our emotional health? It is believed that these microorganisms produce neurotransmitters, such as serotonin and dopamine, which are known to regulate mood and emotions. In fact, the majority of serotonin, often referred to as the “happy hormone,” is produced in the gut. Additionally, the gut microbiota can also produce other chemicals that can affect brain function and mental health.
Furthermore, the gut microbiota can influence the immune system, which plays a crucial role in mental health. Studies have shown that imbalances in the gut microbiota can lead to chronic inflammation, which has been linked to various mental health disorders. By modulating the gut microbiota, it may be possible to reduce inflammation and improve mental well-being.
Understanding the gut-brain connection has opened up new possibilities for the treatment of mental health conditions. Traditional approaches to mental health often focus solely on the brain, using medications that target neurotransmitters. However, emerging research suggests that targeting the gut may also be an effective strategy. Probiotics, which are live bacteria that can benefit the gut microbiota, have shown promise in improving symptoms of depression and anxiety. Additionally, dietary interventions, such as a healthy and balanced diet rich in fiber and fermented foods, can also support gut health and improve emotional well-being.
In conclusion, the gut-brain connection is a fascinating area of research that highlights the importance of gut health in emotional well-being. The gut microbiota and its influence on neurotransmitters, inflammation, and the immune system play a crucial role in mental health. By understanding and harnessing the power of the gut-brain connection, we may be able to develop new approaches for the treatment and prevention of mental health conditions. As awareness of this connection grows, it is essential to prioritize gut health and explore the potential benefits it can have on our emotional well-being.
How Gut Health Influences Cognitive Function and Brain Health
Gut Health Awareness: Understanding the Gut-Brain Connection
The gut-brain connection is a fascinating and complex relationship that has gained significant attention in recent years. It refers to the bidirectional communication between the gut and the brain, where the health of one can greatly influence the other. In particular, gut health has been found to have a profound impact on cognitive function and brain health.
To understand how gut health influences cognitive function, it is important to first recognize the role of the gut in our overall well-being. The gut, also known as the gastrointestinal tract, is responsible for the digestion and absorption of nutrients from the food we consume. It is home to trillions of microorganisms, collectively known as the gut microbiota, which play a crucial role in maintaining a healthy gut.
Research has shown that the gut microbiota not only affects our physical health but also has a significant impact on our mental health. The gut microbiota produces various neurotransmitters, such as serotonin and dopamine, which are essential for regulating mood and emotions. In fact, it is estimated that around 90% of serotonin, a neurotransmitter associated with feelings of happiness and well-being, is produced in the gut.
Furthermore, the gut microbiota also plays a crucial role in the production of short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs), which are important for brain health. SCFAs have been found to have anti-inflammatory properties and can help protect against neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s. They also promote the growth of new brain cells and enhance synaptic plasticity, which is crucial for learning and memory.
However, an imbalance in the gut microbiota, known as dysbiosis, can have detrimental effects on cognitive function and brain health. Dysbiosis can occur due to various factors, including a poor diet, stress, antibiotics, and certain medications. When the gut microbiota is imbalanced, it can lead to increased inflammation, impaired neurotransmitter production, and a compromised blood-brain barrier.
Inflammation, in particular, has been linked to a wide range of mental health disorders, including depression, anxiety, and even schizophrenia. Chronic inflammation in the gut can trigger an immune response that affects the brain, leading to cognitive impairments and mood disturbances. Additionally, a compromised blood-brain barrier can allow harmful substances to enter the brain, further exacerbating cognitive decline.
Fortunately, there are steps we can take to improve gut health and support cognitive function. One of the most effective ways is through a healthy diet. Consuming a diverse range of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and fermented foods can help promote a healthy gut microbiota. Probiotics and prebiotics, which are beneficial bacteria and the food they feed on, respectively, can also be beneficial for gut health.
In addition to diet, managing stress levels is crucial for maintaining a healthy gut-brain connection. Chronic stress can disrupt the balance of the gut microbiota and increase inflammation in the gut. Engaging in stress-reducing activities such as exercise, meditation, and getting enough sleep can help support a healthy gut and improve cognitive function.
In conclusion, understanding the gut-brain connection is essential for maintaining optimal cognitive function and brain health. The gut microbiota and its influence on neurotransmitter production, inflammation, and the blood-brain barrier play a crucial role in shaping our mental well-being. By prioritizing gut health through a healthy diet, stress management, and other lifestyle choices, we can support a healthy gut-brain connection and promote overall well-being.In conclusion, gut health awareness is crucial in understanding the gut-brain connection. The gut and brain communicate through a complex network of nerves, hormones, and chemicals, known as the gut-brain axis. Research has shown that imbalances in gut bacteria can impact mental health, leading to conditions such as anxiety and depression. By promoting gut health through a balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress management, individuals can support their overall well-being and potentially improve their mental health. Increasing awareness about the gut-brain connection is essential for individuals to make informed choices about their lifestyle and prioritize their gut health.